Introduction
When selecting lighting for your home, office, or outdoor spaces, understanding the difference between watts and lumens is essential. Traditionally, people associated brightness with wattage, but with the rise of LED and energy-efficient lighting, lumens have become the new standard for measuring brightness. This guide will help you understand the relationship between watts and lumens, how to choose the right brightness for different applications, and why making the switch to lumens can save energy and money.
What Are Watts and Lumens?
- Watts (W): A watt is a unit of power consumption, measuring how much energy a light source uses. Higher wattage typically meant a brighter light in traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Lumens (lm): Lumens measure the actual amount of visible light produced by a source. The higher the lumens, the brighter the light.
With modern LED and energy-efficient lighting, lower wattages can produce the same or greater brightness as incandescent bulbs, making lumens the best way to measure light output.
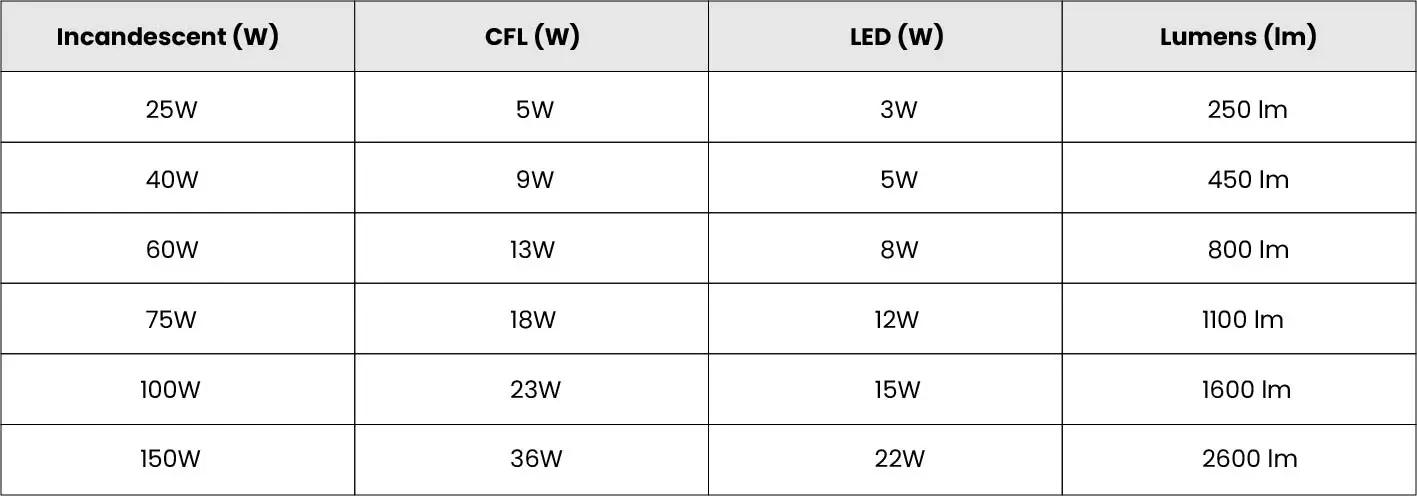
Watts to Lumens Conversion Chart
To help you compare different lighting technologies, here is an approximate conversion of watts to lumens:
Why Lumens Matter More Than Watts
With advancements in LED technology, lighting efficiency has improved significantly. Relying on lumens instead of watts ensures that you get the right amount of brightness while minimizing energy consumption. For example, an LED bulb that uses only 15W can provide the same brightness as a 100W incandescent bulb.
Choosing the Right Brightness for Different Applications
When selecting lighting products, consider the purpose and environment:
- Living rooms & bedrooms: 800–1600 lumens (equivalent to 60W–100W incandescent)
- Kitchens & bathrooms: 1600–2600 lumens for brighter task lighting
- Outdoor lighting: 800+ lumens for pathways, 2000+ lumens for security lighting
- Stadium lighting: 50,000–1,500,000 lumens depending on venue size and level of competition
Energy Savings and Cost Benefits of LED Lighting
Switching from incandescent to LED lighting reduces energy consumption by up to 80%, leading to lower electricity bills and a reduced carbon footprint. LEDs also last significantly longer, with lifespans of 25,000–50,000 hours compared to just 1,000 hours for traditional bulbs.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between watts and lumens helps you make smarter lighting choices, ensuring you get the right brightness while saving energy. Whether you’re illuminating a home, office, or large-scale venue, using lumens as a measurement will help you find the most efficient and effective lighting solutions. Upgrade to LED lighting today and enjoy cost savings, energy efficiency, and superior brightness!